AFCI Outlets – Working to Help Prevent House Fires

We’re all familiar with GFCI outlets, you know, the outlets with the Test and Reset buttons that work to help protect us from electrical shocks. Well, now there’s a new kid in town that helps prevent electrical fires in our homes. It is an Outlet Branch Circuit (OBC) Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) Outlet.

Let’s start by explaining what an arc-fault is. Simply put, it’s an unintentional arcing condition (sparking) that occurs in an electrical circuit. Arcing can create high intensity heat, which may over time ignite surrounding material such as wood framing or insulation. In fact, according to the National Fire Protection Association, arc-faults are “the principle electrical failure mode resulting in fire”.
There are a number of conditions which may cause dangerous arcing to occur, including:
- Damaged wires behind a wall
- Damaged cords that are plugged into an outlet
- Loose electrical connections
- Within electrical cords accidently damaged by furniture or doors pressing or resting on them

What does an OBC AFCI Outlet do?
An OBC AFCI Outlet contains electronic components within the device that constantly monitor a circuit for the presence of “normal” and “dangerous” arcing conditions. If a dangerous arcing condition is detected, the OBC AFCI is triggered to quickly react and cut power to the circuit. The images below depict potentially dangerous arcing, which as you can see is often unseen:
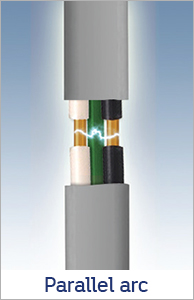

Where would I use an OBC AFCI Outlet?
The 2014 National Electrical Code® mandates AFCI protection in:
- Kitchens
- Family rooms
- Dining rooms
- Living rooms
- Bedrooms
- Parlors
- Libraries
- Dens
- Sunrooms
- Closets
- Hallways
- Laundry areas
- Recreation Rooms
AFCI VS GFCI
OBC AFCI outlets and GFCI outlets look very similar but provide very different protection. It is important to understand the difference as outlined in the table below.
|
OBC AFCI |
GFCI |
|
Provides protection from electrical fires that could result from arc-faults |
Protects users from shocks and electrocution |
|
Detects potentially hazardous arc-faults and quickly cuts off power |
Cuts off power if a ground fault is detected |
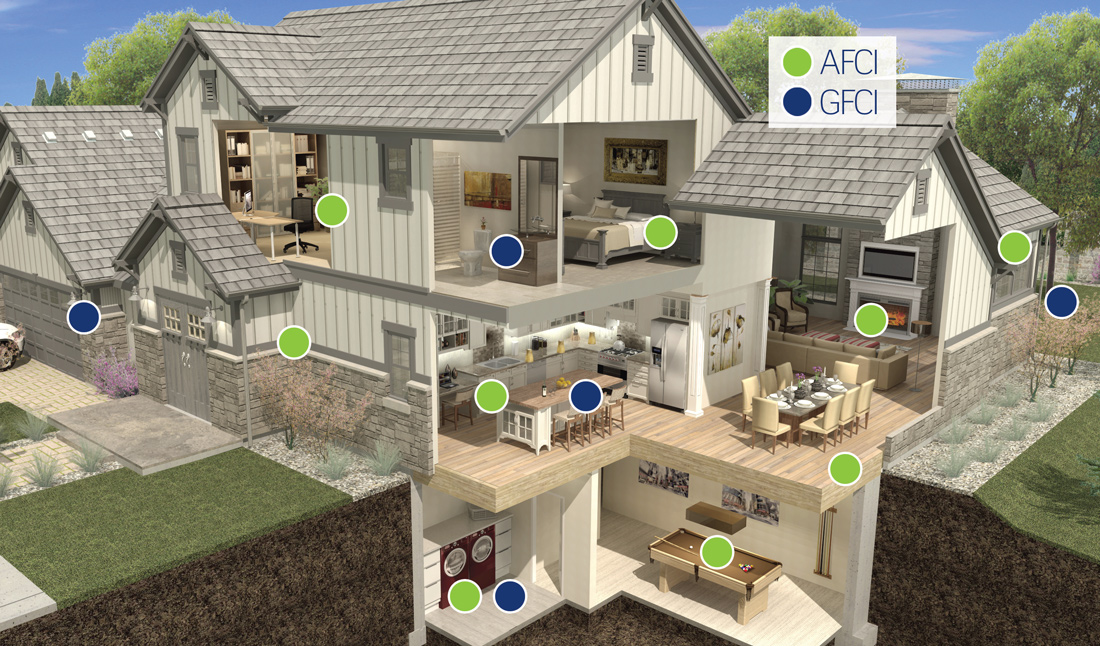
It is also important to be clear on where AFCI and GFCI protection is required in your home. Check out the image below for a snapshot of a typical home.
There’s a lot more to learn about AFCIs. Visit leviton.com/afci and get up to speed on this important safety device.


