What’s Driving Category 6A Adoption?
The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) standard for Category 6A was published in 2008, but the market was initially slow to take off due to high power consumption and cost of first-generation 10GBASE-T PHYs and equipment. However, in the past few years, Cat 6A adoption has increased dramatically, becoming the dominant media type for 10 Gb/s networks. And when comparing costs per port of equipment, maintenance, and assembly of 10G Ethernet, Cat 6A and twisted pair is significantly more cost-effective than other technologies. Today’s Cat 6A cable is also much smaller in diameter and lighter in weight than early generations, improving fill capacity and creating more flexibility for a tighter bend radius.
Category 6A will continue to see strong growth in the years to come, especially in the following environments and applications.
 Data Centers
Data Centers
Data centers everywhere are moving quickly to address bandwidth growth. Many data center managers looking to control costs are choosing Cat 6A twisted pair copper for 10 Gb/s applications, since it is the most cost-effective option for access layer networking. In fact, the cost of 10GBASE-T channels is at least 30% lower than alternative SFP+ channels.
Cat 6A also makes migration easy. 10GBASE-T allows for auto-negotiation, so two Ethernet devices can connect to each other and select a common transmission speed that both device support. This allows for 10GBASE-T migration to be done in phases for a portion of the network or during a complete network upgrade, giving data center managers some flexibility in terms of timing, disruption, and cost for upgrading the network.
As with previous industry migrations to 1 and 10Gb/s, copper systems will remain a key part of the transition to 25 and 40 Gb/s. In June 2016, The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) approved standards defining Cat 8, supporting data center networks up to 40 Gb/s. While Cat 8 supports future applications, Cat 6A has become the dominant copper cabling solutions in data centers today.
Enterprise Wireless
More businesses are updating their wireless networks with 802.11ac access points, capable of delivering up to 6.9 Gb/s. In 2015, sales of 802.11ac access points were up 10 fold over 2014, according to Broadcom.
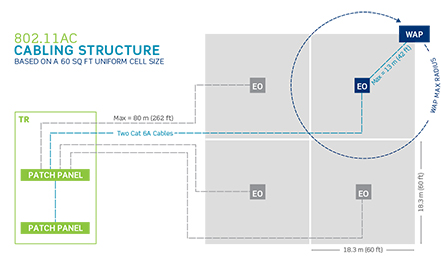
However, businesses won't see the true benefits of these higher speeds without the right cabling infrastructure, which is why TIA TSB-162-A, Telecommunications Cabling Guidelines for Wireless Access Points, recommends installing Cat 6A for horizontal cabling to WAPs. TSB-162-A also recommends using a grid-based zone cabling architecture, with at least two Cat 6A cable runs to each cell in the grid. Two cable runs will ensure backup power to the WAP in PoE applications, and prepare the infrastructure for future expansion and data requirements.
In October 2016, IEEE published the 802.3bz standard for 2.5GBASE-T and 5GBASE-T, using Category 5e and 6 cabling. While the new standard could extend use of installed Category 5 and 6 cabling, there will likely be limitations. Category 6A remains the recommended cabling for all new installations. It will support greater lengths, and provide greater alien crosstalk suppression at higher frequencies. Businesses that upgrade their backbone cabling infrastructure today with Cat 6A cabling based on TSB-162-A recommendations will not only prepare their workplaces for 802.11ac wireless, but will be ready for 2.5 Gb/s, 5 Gb/s, and 10 Gb/s applications in the future.

Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) has made great strides in recent years. Driven by the demand for ease of installation and boosted by new standards that expand support to more devices, PoE is seeing explosive growth rates that match the period shortly after the technology was initially introduced in 2003. However, higher current PoE brings important cabling and connectivity considerations when ensuring utmost performance in the network.
Horizontal cables and patch cords with the largest conductors available (i.e., the lowest wire gage number) will improve the current flow, generating less heat than smaller conductors. A higher category rating will typically have larger conductor sizes, providing advantages where there are concerns about bundle temperature rise. For this reason, Cat 6A cabling is recommended for all new PoE installations.
You will likely need a cabling infrastructure that can deliver more power in the future. Leviton Atlas-X1 connectivity has been tested to deliver 100-watt PoE, allowing or driving power and data to a wider range of remote devices.
Health Care Networks
Hospitals are seeing huge jumps in data growth, largely due to the rise of Electronic Health Records, as well as more connected equipment at the bedside and other areas. Cat 6A cabling offers the best solution for hospitals seeking system longevity, faster data transfer, and support for high-bandwidth wireless networks. By supporting network speeds of 10 Gb/s, Cat 6A can dramatically reduce the time it takes to access information such as medical images, translating into more efficient diagnosis and collaboration. For these reasons it is the recommended cabling system in the ANSI/TIA-1179 health care infrastructure standard. In the upcoming 1179-A revision (2017 estimated release), Cat 6A will be the only recognized copper cabling for horizontal cabling in health care facilities.
There is also a huge push to support staff, patients, and visitors with reliable wireless access. This means that the wired infrastructure to support Wi-Fi has become a bigger priority for IT departments. Hospitals will not see the full benefits of new wireless technology without the right cabling infrastructure behind it. And as mentioned earlier, only Category 6A will support future migration to speeds up to 6.9 Gbps offered by 802.11ac technologies.
Schools and Universities
High-speed internet is vital for supporting student education at all levels. Whether performing online research for papers, giving in-class presentations, or engaging in extracurricular learning, students need greater bandwidth for quick access to information in order to achieve their goals. That is why Leviton recommends Cat 6A cabling as the backbone for new school network installations.
In classrooms and university lecture halls, AV systems increasingly use HDBaseT technology to extend HDMI, VGA, and USB signals from teachers' desks to the latest devices anywhere in the room, all networked over easy-to-install category-rated cable. However, Leviton testing has found that Cat 5e cabling in HDBaseT applications can lead to high packet error rates and total link loss, as the channels are not designed for resistance to alien crosstalk. Even Cat 6 cables can be limited in carrying HDBaseT signals when adjacent to other cables carrying HDBaseT.
Cat 6A cabling is the best solution for protecting signals in cable bundles from alien crosstalk issues. Cat 6A also supports the higher bandwidth signals for applications such as 4K, creating a future-proof installation and best return on infrastructure investment.
Make the Smart Choice for Cat 6A Systems
Data centers, businesses, government agencies, hospitals, and schools all require higher performance networks and greater bandwidth to meet today's data demand. Leviton has designed Cat 6A systems for these demanding networks. Our UTP and shielded solutions all meet IEEE, TIA, and ISO/IEC requirements for mission critical networks running at 10Gb/s, and performance has been verified by independent testing labs. You can learn more about Leviton systems at Leviton.com/Cat6A.


